Message Sequence Charts (MSC)
Message Sequence Charts (MSC) is a graphical language for the description and specification of the interactions
between system components. These interactions usually include typical or exceptional message
flows between communicating entities. The language is standardized by the
ITU-T as
ITU Recommendation Z.120.
MSCs have long been used in standardization and in industry for visualization of selected
message traces. Its simplicity and intuitive understanding have made the notation quite popular.
MSCs are often used in combination with
SDL where MSCs diagrams and
related SDL descriptions should be regarded as different but complementary views
of a system. SDL provides behaviour descriptions of individual entities, but
there is no direct description of communication between communicating entities.
By contrast, MSCs provide a clear description of communication traces in the
form of message flows.
Despite their simplicity, MSCs are a powerful notation, with built-in
mechanisms to portray timers, loops, optional, alternative and exceptional
system behaviour, as is necessary in any protocol description.
Message Sequence Charts may be used for requirement specification, display of
simulation and validation traces, test-case specification and documentation of
real-time systems.
Use of MSC tools
MSC diagrams can be drawn using any computer application capable of handling
simple graphics. However, the use of specialized MSC tools improves all aspects
of their development and use. It enforces the use of standardized MSC language
elements, while permitting rapid development and maintenance of diagrams.
Including MSC diagrams into the text of the standard is very straightforward.
High Level Message Sequence Charts (HMSC)
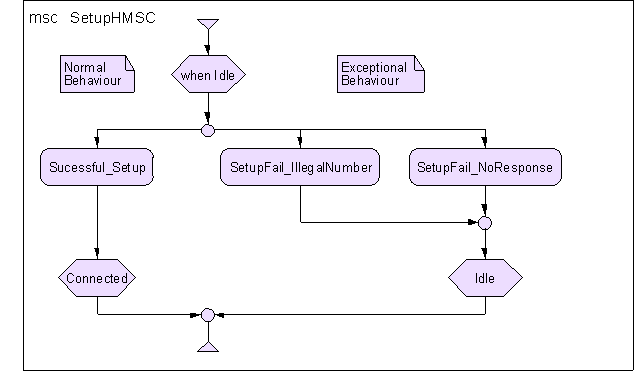
The Z.120 standard also defines High Level Message Sequence Charts (HMSCs).
HMSC diagrams are used to specify more complex patterns of message flows by
showing sequences or alternatives of atomic MSC scenarios, shown only as MSC
references. HMSC diagrams specify the composition of communication activities
that are needed while the referenced MSC diagrams show how the communication is
done in terms of message sequences. HMSC diagrams can conveniently express
options and alternatives in using parts of a complex procedure. Expressing the
same thing only in MSC diagrams is possible but less straightforward.
ETSI Guidance on the use of MSC
A guideline for the use of MSC in communication standardization is available
within the guidelines for SDL,
EG 202 106, drafted by ETSI technical committee Methods for Testing and
Specification (MTS).
MSCs and UML sequence diagrams address the same needs and are in many ways
similar, however, there are differences between the two. In MSCs the vertical
lines represent autonomous execution entities while in Sequence diagrams they
usually represent an object. In MSCs an arrow is an asynchronous message while
in sequence diagrams it is usually a synchronous operation call on an object.
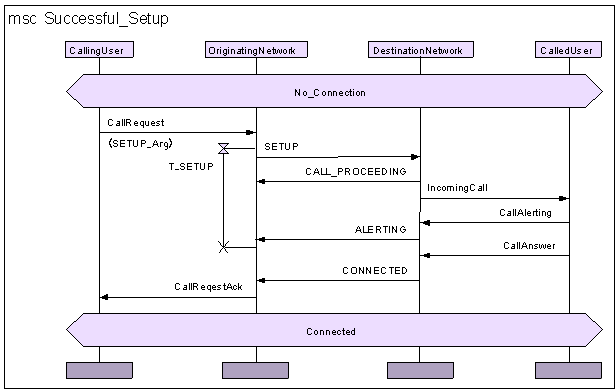
Example MSC diagram